Why Telemedicine Is Important
The United States does not have enough doctors, and the problem is getting worse. In the future, many people may not be able to see a doctor when they need one. Telemedicine helps fix this problem by letting doctors talk to patients online and give care from far away.
Telemedicine apps let people talk to doctors from their homes. Patients do not need to travel or wait a long time. This is especially helpful for people living in villages, small towns, or faraway places.
In this guide, we explain why telemedicine is helpful and how to build a telemedicine app.
What Is Telehealth Software?
Telemedicine started many years ago. In the 1940s, doctors first sent medical images using phone lines. This helped doctors share information faster.
Today, telemedicine means using phones, computers, and the internet so doctors and patients can talk. This includes video calls, messages, and remote health monitoring. Smart devices can now check a patient’s health even when they are at home.
Medicine is changing, and telemedicine helps meet people’s new healthcare needs.
Telemedicine Market Overview
Telemedicine is growing very fast. In 2024, the industry was worth over $161 billion, and it continues to grow every year. North America is the biggest user of telemedicine.
This growth happens because:
-
More people have long-term illnesses
-
Doctors want to monitor patients from far away
-
Some areas do not have enough doctors
-
COVID-19 made online healthcare more common
Types of Telemedicine Apps
Here are common types of telemedicine apps explained simply:
Tele-ICU
Doctors monitor very sick patients in hospitals from far away using cameras and medical devices.
Surgical Telemedicine
Doctors can help perform surgeries using robots and special machines, even if they are not in the same room.
Telerehabilitation
Patients do therapy exercises at home while doctors watch and guide them online.
Teleoncology
Cancer doctors share test results and talk to patients online instead of always meeting in person.
Virtual Second Opinions
Patients send their medical reports online and get advice from expert doctors.
Telepsychiatry
Mental health doctors talk to patients through video calls to help with stress, anxiety, or depression.
Teleradiology
Doctors look at X-rays, MRIs, and scans from anywhere in the world.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Smart devices check things like heart rate and blood pressure and send the data to doctors.
Teledermatology
Doctors examine skin problems using high-quality photos and cameras.
Telepathology
Doctors study tissue samples digitally instead of using microscopes in labs.
Teleophthalmology
Eye doctors check vision and eye health using special cameras and machines.
Telecardiology
Heart doctors monitor heart activity and give advice online.
Teledentistry
Dentists check teeth and gums using cameras and online tools.
Telenephrology
Kidney specialists treat patients online and monitor dialysis remotely.
Teleneurology
Brain and nerve doctors help patients online, especially during emergencies like strokes.
Benefits of Telemedicine Apps
Benefits for Patients
-
Talk directly to doctors online
-
No need to travel
-
Lower medical costs
-
Works on phones, tablets, and computers
Benefits for Doctors
-
Easy teamwork with other doctors
-
Monitor patients at home
-
Handle more appointments
-
Fewer missed appointments
-
Works with hospital systems
Popular Telemedicine Apps
-
Teladoc Health – Offers many healthcare services in one app
-
Amwell – Works well with hospitals and clinics
-
MDLive – Gives fast access to doctors for everyday health needs
How Telemedicine Is Changing Healthcare
Telemedicine helps doctors treat more patients and make better decisions. Video calls, messages, and smart tools improve care. Artificial intelligence can help find health risks early and suggest treatments.
This makes healthcare more personal and effective.
How to Build a Telemedicine App (Simple Steps)
Step 1: Research the Market
Find out who will use the app—patients or doctors—and what problems it should solve.
Step 2: Decide What the App Will Do
Choose important features first. Remove anything not needed. Make sure the app follows healthcare laws.
Step 3: Choose How to Build It
Use Agile methods so changes can be made easily. Pick the right team and set deadlines.
Step 4: Create a Simple Version (MVP)
Build a basic app to test how it works. This saves time and money.
Step 5: Build and Test the Full App
Add all features and test the app carefully with real users.
Challenges and Simple Solutions
Connecting With Hospital Systems
Use standard formats so the app works with hospital records.
Making the App Easy to Use
Test the app, keep the design simple, and add features for people with disabilities.
Internet Problems
Make the app work on slow internet and older devices.
Language Problems
Add support for multiple languages.
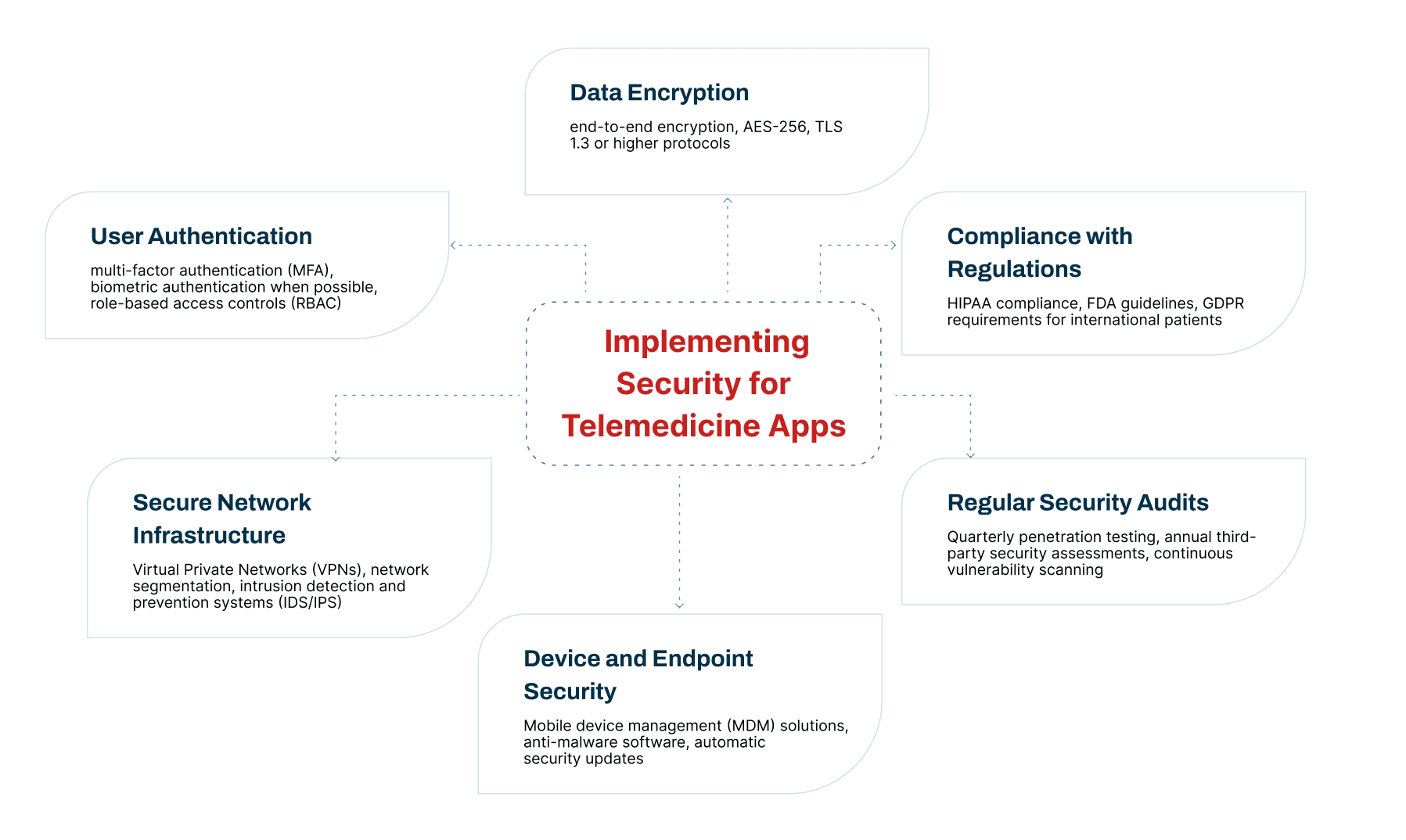
Keeping Data Safe
Protect patient information using strong security and privacy rules.
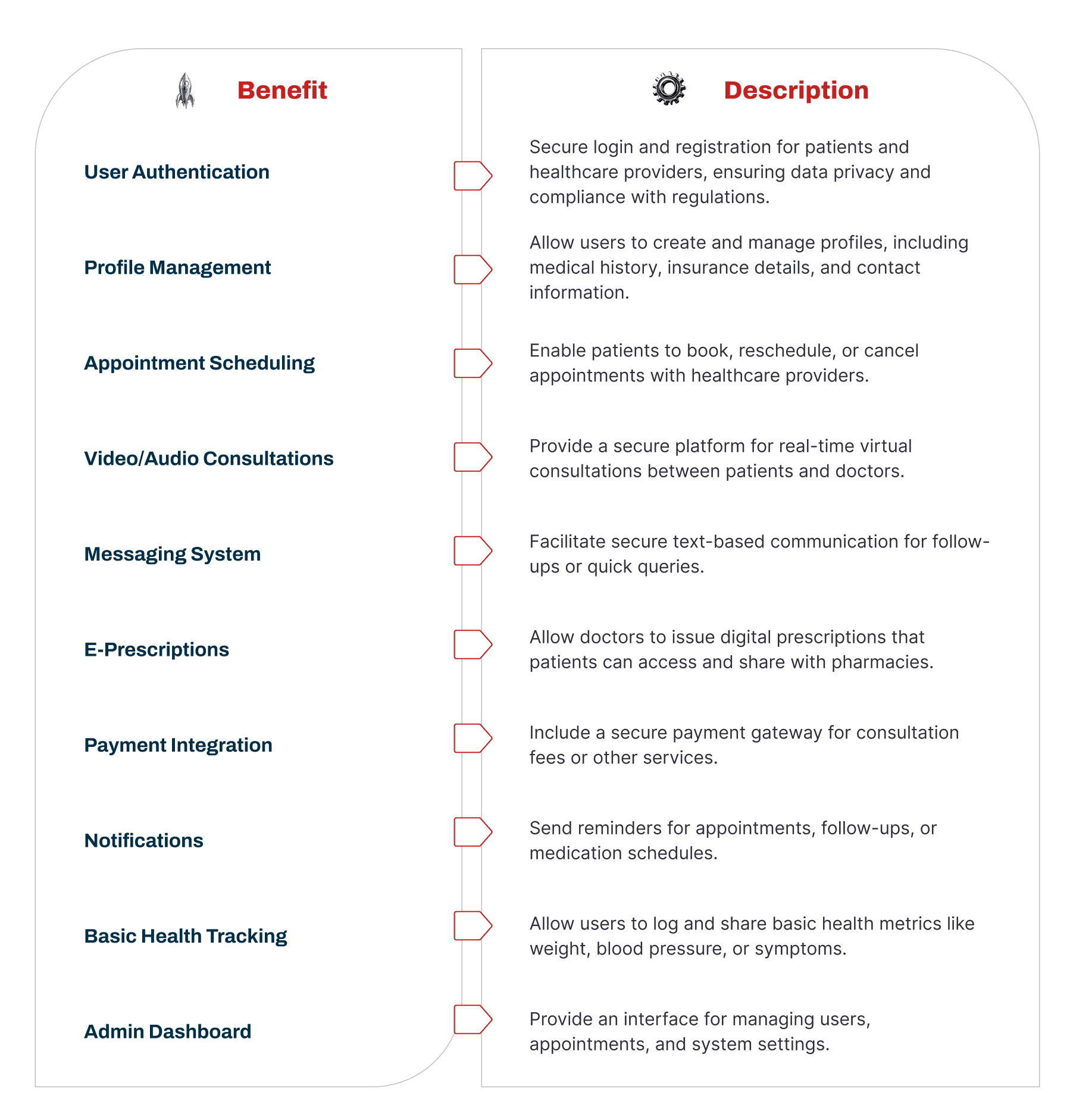
Main Technologies and Features of a Telehealth App
A telehealth app needs the right tools and features to work well. These features help patients, doctors, and healthcare providers feel happy using the app and make sure it follows all rules.
Basic Features (MVP Features)
When building a telehealth app, you should first include the most important features. These basic features help people start using the app easily and help the app grow faster.
Having a strong base of simple and useful features makes more people want to use the app and helps it become popular.

Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Telemedicine App (With AST Services)
Building a telemedicine app needs a clear plan and the right team. Ast Services uses smart methods, modern tools, and clear goals to make useful healthcare apps. Here is how the process works in simple steps.
Step 1: Set Goals and Plan the App
First, we decide what the app should do and who it will help.
We study the healthcare market to find problems people face when getting medical care.
To build the first version of the app (called MVP), we decide:
-
How well the app should work
-
How big it can grow in the future
-
How it will connect with other hospital systems
All of this is written down so future work stays on track.
Step 2: Follow Healthcare Rules
Healthcare apps must follow strict safety laws like HIPAA.
The app must:
-
Protect patient health data
-
Track who uses the data and when
-
Keep records of access and activity
-
Warn users if there is a data problem
This keeps patient information safe.
Step 3: Choose the Right Technology
iOS or Android
-
iOS users often spend more money on apps
-
Android is used by more people worldwide
Many apps support both.
App or Website
-
Desktop apps work offline and are powerful
-
Web apps are easier to update and maintain
SaaS or Custom App
-
SaaS apps are faster and cheaper but less flexible
-
Custom apps give more control but cost more
Step 4: Design the App (UX & UI)
The app must be easy to use.
If it is confusing, people will stop using it.
-
UX (User Experience): Learn what users like and dislike
-
UI (User Interface): Keep the design clean, simple, and professional
Step 5: Build the Basic Telemedicine Features
Video calls are the heart of telemedicine.
The app should support:
-
Clear video and audio calls
-
Automatic video quality adjustment
-
File sharing and screen sharing (when allowed by law)
Step 6: Add Strong Security
Following rules is not enough—you must protect data strongly.
The app should:
-
Prevent hacking
-
Keep patient data private
-
Protect the system from attacks
This helps keep trust and long-term success.
Step 7: Add Extra Features Using APIs
APIs are tools that add ready-made features. Popular ones include:
-
VSee – Secure video calls for healthcare
-
VIDYO – High-quality video and security
-
WebRTC – Real-time video and chat
-
OpenTok – Video with healthcare safety features
-
Twilio – Messaging, video, voice, and security
-
Acuity – Appointment booking and payments
Step 8: Build a Test Version (Prototype)
Before finishing the app, a test version is built.
This helps:
-
Check if features work
-
Find problems early
-
Save time and money
Doctors and patients test it before full development.
Step 9: Get Approvals and Certifications
Some healthcare apps need official approval (like FDA approval).
Experts help:
-
Prepare documents
-
Run safety tests
-
Meet state and national rules
This step makes sure the app is legal to use.
Step 10: Launch and Maintain the App
When the app is ready, it goes live.
After launch:
-
Track how people use it
-
Fix problems quickly
-
Update features without breaking rules
-
Keep data safe
White Label Telemedicine Apps (Ready-Made Apps)
Some companies use ready-made telemedicine apps and add their own branding.
These apps usually include:
-
Custom logo and colors
-
Separate doctor and patient accounts
-
Video and audio consultations
-
Appointment booking
-
Online payments
-
Digital prescriptions
-
Access to patient medical records
These save time and money.
Business Model for a Telemedicine App
A good telemedicine app is not just about technology—it’s also about business.
A business model helps decide:
-
How the app makes money
-
Who uses it
-
What value it offers
This ensures long-term success.


